百度面试
1、Two Sum 两数和问题
Given an array of integers, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number.
Input: numbers={2, 7, 11, 15}, target=9 Output: index1=1, index2=2
(1)、暴力法 Brute Force
复杂度:O(1)空间 O(n^2)时间
思路:通过双重循环遍历数组中所有元素的两两组合,当出现符合的和时返回两个元素的下标
注意:内层循环要从外层循环下标加一开始,避免遍历到两个相同的元素
(2)哈希表 Hash_map(STL)
复杂度:O(n)空间 O(n)时间
思路:第一次遍历数组先将所有元素和它的下标作为key-value对存入Hashmap中,第二次遍历数组时根据目标和与当前元素之差,在Hashmap中找相应的差值。如果存在该差值,说明存在两个数之和是目标和。此时记录下当前数组元素下标并拿出Hashmap中数组元素下标即可。Hashmap获取元素的时间复杂度是O(1),所以总的时间复杂度仍不超过O(n)。
注意:
1、判定是否存在该差值时,要同时判断该差值的下标是不是当前遍历的元素下标,以避免重复
2、哈希表作为一个Collection,初始化时请注意声明Key和Value的类型
#include <iostream>
#include <hash_map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
hash_map<int,int> hashmap;
const int n=5;
int a[n]={1,4,2,3,5};
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
hashmap[a[i]]=i;
int t=9;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int tmp=t-a[i];
hash_map<int,int>::iterator it;
it=hashmap.find(tmp);
if(it!=hashmap.end()&&i<it->second){
cout<<i<<" "<<it->second<<endl;
}
}
system("pause");
}
(3)、排序双指针法 Sorting with Two Pointers
复杂度:O(n)空间 O(nlogn)时间
思路:首先将原数组复制一遍,对新数组进行排序。排序后将双指针指向头部与尾部元素,进行迭代。如果双指针指向元素之和大于目标和,则将尾部指针向前移一位,反之则将头部指针向后移一位,直到双指针指向元素之和等于目标和,记录这两个元素的值,然后再遍历一遍旧数组,找出这两个元素的下标。
注意:该方法需要先将结果数组都初始化为-1,否则在遍历旧数组时无法去除重复,可能会将两个下标都存入同一个结果中
2、3Sum 三数和问题
复杂度:时间 O(N^2) 空间 O(1)
思路:3Sum其实可以转化成一个2Sum的题,我们先从数组中选一个数,并将目标数减去这个数,得到一个新目标数。然后再在剩下的数中找一对和是这个新目标数的数,其实就转化为2Sum了。为了避免得到重复结果,我们不仅要跳过重复元素,而且要保证2Sum找的范围要是在我们最先选定的那个数之后的。
3、3Sum Closet 三和最接近问题
复杂度:时间 O(N^2) 空间 O(1)
思路:和3Sum的解法一样。在3Sum中,我们只有找到和目标完全一样的时候才返回,但在Closet中,我们要记录一个最小的差值,并同时记录下这个最小差值所对应的和。
4、Search Insert Position
Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
You may assume no duplicates in the array.
Here are few examples.
[1,3,5,6], 5 → 2
[1,3,5,6], 2 → 1
[1,3,5,6], 7 → 4
[1,3,5,6], 0 → 0
思路:
-
二分法变形, 最讨厌的题目, 总是搞不清该返回 low 还是 high
-
若是真的要解释话. 最终 low == high, 这个时候, Mid = low = high. 假如 A[mid]>target, 那么插入位置就是 mid 处, 返回 low, OK. 假如 A[mid] < target, 那么 low = mid+1, 仍然返回 low
-
二分法的题目, 总是不能随心所欲
class Solution {
public:
int searchInsert(int A[], int n, int target) {
return bSearch(A, n, target);
}
int bSearch(int A[], int n, int target) {
int low = 0, high = n-1;
while(low <= high) {
int mid = (low+high)>>1;
if(A[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if(A[mid] > target)
high = mid-1;
else
low = mid+1;
}
if(high < 0) return 0;
if(low >= n) return n;
return low;
}
};
5、Trapping Rain Water
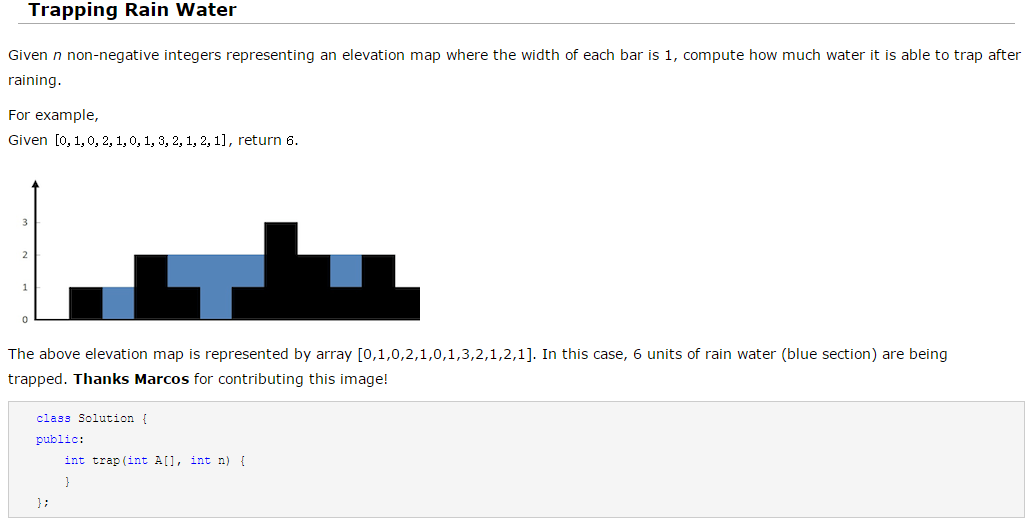
题目不难,观察下就可以发现被水填满后的形状是先升后降的塔形,因此,先遍历一遍找到塔顶,然后分别从两边开始,往塔顶所在位置遍历,水位只会增高不会减小,且一直和最近遇到的最大高度持平,这样知道了实时水位,就可以边遍历边计算面积。
6、指针和引用的区别
7、STL 内存分配方式
8、仿函数有什么用,和函数指针有什么不同,哪个效率高
9、进程线程的区别
10、TCP UDP的不同 TCP三次握手
11、select和epoll区别,select为什么慢
12、一开始就让写了个快速排序
13、项目中有没有见过内存泄漏?为什么会产生?怎么解决的?
14、写了一个约瑟夫环问题的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int total = 0;
cin >> total;
int number = 0;
cin >> number;
list<int> * table = new list<int>();
for(int i = 1; i <= total; ++i) {
table->push_back(i);
}
int shout = 1;
int last = 0;
list<int>::iterator next;
for(list<int>::iterator it = table->begin() ; !table->empty();) {
if(shout++ == number) {
last = *it;
it=table->erase(it);
shout = 1;
}
else
it++;
if(it == table->end())
it = table->begin();
}
cout << last << endl;
}
15、红黑树的原理
16、volatile关键字的原理