树型结构是一种重要的非线性数据结构。其中以树和二叉树最为常用,直观来看,树是以分支关系定义层次结构。树在计算机领域中得到广泛的应用,如在编译程序中,可用树来表示源程序的语法结构;在数据库系统中,树型结构也是信息的重要组织形式之一。
树的定义
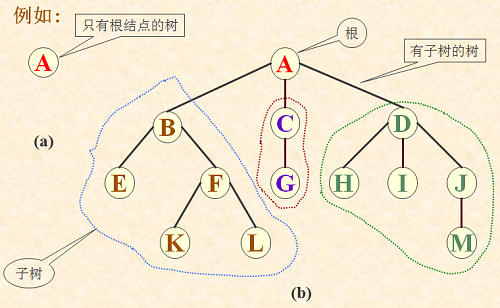
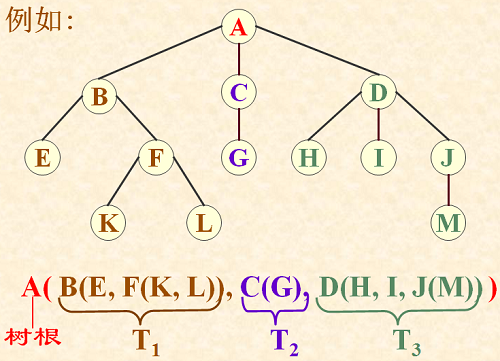
树(tree)是n(n≥0)个结点的有限集。
1)有且仅有一个特定的称为树根(root)的结点;
2)当n>1时,其余结点可分为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集T1,T2,…Tm,其中每一个集合本身又是一棵树,称为根的子树(SubTree).
特点:
(1).在非空树中至少有一个结点—根;
(2).树中各子树是互不相交的集合.
相关概念:
结点:数据元素及若干指向子树的分支;
结点的度:分支(子树)的个数;
树的度:树中所有结点的度的最大值;
叶子结点:度为零的结点;
分支结点:度大于零的结点。
结点的层次:假设根结点的层次为1,第l 层结点的子树的根在第l+1层;
树的深度:树中叶子结点所在的最大层次;
森林:是 m(m≥0)棵互不相交的树的集合:
任何一棵非空树是一个二元组 Tree=(root,F)
其中:root 被称为根结点,F 被称为子树森林;
树型结构与线性结构的比较:

二叉树
二叉树的定义
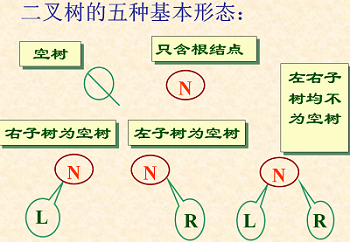
定义:二叉树(Binary Tree)是一种树型结构,它的特点是每个结点至多只有两颗子树,即二叉树中不存在度大于2的结点,并且,二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒。
二叉树的性质
性质1:
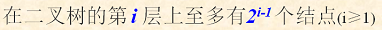
性质2:

性质3:

以上三个性质可以以任意一个二叉树进行证明。
性质4:

性质5:

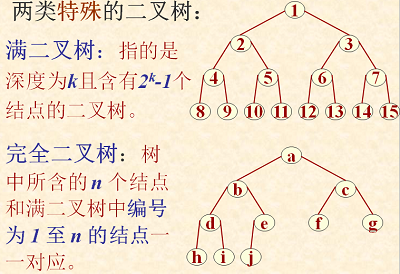
两种特殊的二叉树:
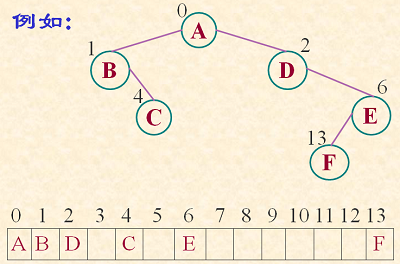
二叉树的顺序存储结构
用一组地址连续的存储单元依次自上而下,自左至右存储二叉树的结点元素,即将二叉树上编号为i的结点元素存储在定义的一维数组中下标为i-1的分量中。
二叉树顺序存储结构:
#define MAX_TREE_SIZE 100 //二叉树的最大结点数
typedef int TElemType;
typedef TElemType SqBiTree[MAX_TREE_SIZE]; //0号单元存储根结点
SqBiTree bt;
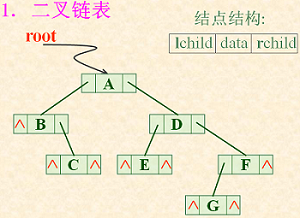
二叉树的二叉链表存储结构:
typedef struct BiTNode{
TElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild,*rchild; //左右孩子指针
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
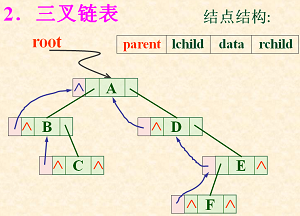
二叉树的三叉链表存储结构:
typedef struct TriTNode { // 结点结构
TElemType data;
struct TriTNode *lchild,*rchild; // 左右孩子指针
struct TriTNode *parent; //双亲指针
}TriTNode, *TriTree;
二叉树的创建
采用前序的方式进行创建:
Status CreateTree(BiTree &T){
int num;
cin>>num;
if(num==0){
T=NULL;
}else{
T=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
T->data=num;
CreateTree(T->lchild);
CreateTree(T->rchild);
}
return OK;
}
二叉树的遍历
先(根)序的遍历算法:
若二叉树为空树,则空操作;否则,
(1)访问根结点;
(2)先序遍历左子树;
(3)先序遍历右子树。
递归实现先序遍历:
void DgPreVist(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
cout<<T->data<<" ";
DgPreVist(T->lchild);
DgPreVist(T->rchild);
}
}
前序非递归遍历二叉树:
根据前序遍历访问的顺序,优先访问根结点,然后再分别访问左孩子和右孩子。即对于任一结点,其可看做是根结点,因此可以直接访问,访问完之后,若其左孩子不为空,按相同规则访问它的左子树;当访问其左子树时,再访问它的右子树。因此其处理过程如下:
对于任一结点P:
(1)访问结点P,并将结点P入栈;
(2)判断结点P的左孩子是否为空,若不为空,则将P的左孩子置为当前的结点P,循环至(1);若为空,则取栈顶结点并进行出栈操作,并将栈顶结点的右孩子置为当前的结点P,循环至(1);
(3)直到P为NULL并且栈为空,则遍历结束。
void FDgPreVist(BiTree T){
vector<BiTree> s; //声明vector当作栈使用
BiTree p=T;
while(p!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(p!=NULL){
cout<<p->data<<" "; //访问
s.push_back(p); //入栈
p=p->lchild;
}
if(!s.empty()){
int len=s.size();
p=s[len-1];
p=p->rchild; //右孩子
s.pop_back(); //出栈
}
}
}
中(根)序的遍历算法:
若二叉树为空树,则空操作;否则,
(1)中序遍历左子树;
(2)访问根结点;
(3)中序遍历右子树。
中序递归遍历二叉树:
void DgInVist(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
DgInVist(T->lchild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
DgInVist(T->rchild);
}
}
中序非递归遍历二叉树:
根据中序遍历的顺序,对于任一结点,优先访问其左孩子,而左孩子结点又可以看做一根结点,然后继续访问其左孩子结点,直到遇到左孩子结点为空的结点才进行访问,然后按相同的规则访问其右子树。因此其处理过程如下:
对于任一结点P:
(1)若其左孩子不为空,则将P入栈并将P的左孩子置为当前的P,然后对当前结点P再进行相同的处理,循环至(1);
(2)若其左孩子为空,则取栈顶元素并进行出栈操作,访问该栈顶结点,然后将当前的P置为栈顶结点的右孩子,循环至(1);
(3)直到P为NULL并且栈为空则遍历结束。
void FDgInVist(BiTree T){
vector<BiTree> s; //声明vector当作栈使用
BiTree p=T;
while(p!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(p!=NULL){
s.push_back(p); //入栈
p=p->lchild;
}
if(!s.empty()){
int len=s.size();
p=s[len-1];
cout<<p->data<<" "; //访问
p=p->rchild; //右孩子
s.pop_back(); //出栈
}
}
}
后(根)序的遍历算法:
若二叉树为空树,则空操作;否则,
(1)后序遍历左子树;
(2)后序遍历右子树;
(3)访问根结点。
后序递归遍历二叉树:
void DgPostVist(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
DgPostVist(T->lchild);
DgPostVist(T->rchild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
}
}
后序非递归遍历二叉树:
要保证根结点在左孩子和右孩子访问之后才能访问,因此对于任一结点P,先将其入栈。如果P不存在左孩子和右孩子,则可以直接访问它;或者P存在左孩子或者右孩子,但是其左孩子和右孩子都已被访问过了,则同样可以直接访问该结点。若非上述两种情况,则将P的右孩子和左孩子依次入栈,这样就保证了每次取栈顶元素的时候,左孩子在右孩子前面被访问,左孩子和右孩子都在根结点前面被访问。
void FDgPostVist(BiTree T){
vector<BiTree> s;
BiTree cur; //当前结点
BiTree pre=NULL; //前一次访问的结点
s.push_back(T);
while(!s.empty()){
int len=s.size();
cur=s[len-1]; //获取栈顶结点
if((cur->lchild==NULL&&cur->rchild==NULL)||
(pre!=NULL&&(pre==cur->lchild||pre==cur->rchild))){
cout<<cur->data<<" "; //打印当前结点
s.pop_back();
pre=cur; //录当前打印结点
}else{
if(cur->rchild!=NULL)
s.push_back(cur->rchild); //有孩子先进栈
if(cur->lchild!=NULL)
s.push_back(cur->lchild);
}
}
}
完整代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef int TElemType;
typedef int Status;
//函数结果状态代码
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
//二叉树的链表存储结构
typedef struct BiTNode{
TElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild,*rchild; //左右孩子指针
}BiTNode,*BiTree;
//创建二叉树
Status CreateTree(BiTree &T){
int num;
cin>>num;
if(num==0){
T=NULL;
}else{
T=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
T->data=num;
CreateTree(T->lchild);
CreateTree(T->rchild);
}
return OK;
}
//前序递归遍历二叉树
void DgPreVist(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
cout<<T->data<<" ";
DgPreVist(T->lchild);
DgPreVist(T->rchild);
}
}
//前序非递归遍历二叉树
void FDgPreVist(BiTree T){
vector<BiTree> s; //声明vector当作栈使用
BiTree p=T;
while(p!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(p!=NULL){
cout<<p->data<<" "; //访问
s.push_back(p); //入栈
p=p->lchild;
}
if(!s.empty()){
int len=s.size();
p=s[len-1];
p=p->rchild; //右孩子
s.pop_back(); //出栈
}
}
}
//中序递归遍历二叉树
void DgInVist(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
DgInVist(T->lchild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
DgInVist(T->rchild);
}
}
//中序非递归遍历二叉树
void FDgInVist(BiTree T){
vector<BiTree> s; //声明vector当作栈使用
BiTree p=T;
while(p!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(p!=NULL){
s.push_back(p); //入栈
p=p->lchild;
}
if(!s.empty()){
int len=s.size();
p=s[len-1];
cout<<p->data<<" "; //访问
p=p->rchild; //右孩子
s.pop_back(); //出栈
}
}
}
//后序递归遍历二叉树
void DgPostVist(BiTree T){
if(T!=NULL){
DgPostVist(T->lchild);
DgPostVist(T->rchild);
cout<<T->data<<" ";
}
}
//后序非递归遍历二叉树
void FDgPostVist(BiTree T){
vector<BiTree> s;
BiTree cur; //当前结点
BiTree pre=NULL; //前一次访问的结点
s.push_back(T);
while(!s.empty()){
int len=s.size();
cur=s[len-1]; //获取栈顶结点
if((cur->lchild==NULL&&cur->rchild==NULL)||
(pre!=NULL&&(pre==cur->lchild||pre==cur->rchild))){
cout<<cur->data<<" "; //打印当前结点
s.pop_back();
pre=cur; //录当前打印结点
}else{
if(cur->rchild!=NULL)
s.push_back(cur->rchild); //有孩子先进栈
if(cur->lchild!=NULL)
s.push_back(cur->lchild);
}
}
}
int main(){
BiTree T;
CreateTree(T);
FDgPreVist(T);
cout<<endl;
FDgInVist(T);
cout<<endl;
FDgPostVist(T);
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
}
使用栈来实现树的层序遍历
由二叉树的先序和中序序列建树
仅知二叉树的先序序列“abcdefg” 不能唯一确定一棵二叉树,如果同时已知二叉树的中序序列“cbdaegf”,则会如何?


二叉树C++代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int n):val(n){
left=NULL;
right=NULL;
}
};
void preVist(TreeNode *T){ //递归先序遍历
if(T!=NULL){
cout<<T->val<<" ";
preVist(T->left);
preVist(T->right);
}
}
void preVistf(TreeNode *T){ //非递归先序遍历
if(T!=NULL){
stack<TreeNode*> Q;
TreeNode *p=T;
while(p!=NULL||!Q.empty()){
while(p!=NULL){
cout<<p->val<<" ";
Q.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
if(!Q.empty()){
p=Q.top()->right;
Q.pop();
}
}
}
}
void inVist(TreeNode *T){ //递归中序遍历
if(T!=NULL){
inVist(T->left);
cout<<T->val<<" ";
inVist(T->right);
}
}
void inVistf(TreeNode *T){ //非递归中序遍历
if(T!=NULL){
stack<TreeNode*> s;
TreeNode *p=T;
while(p!=NULL||!s.empty()){
while(p!=NULL){
s.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
if(!s.empty()){
cout<<s.top()->val<<" ";
p=s.top()->right;
s.pop();
}
}
}
}
//根据先序遍历和中序遍历递归实现构造二叉树
void PreIndfs(vector<int> prevec,vector<int> invec,TreeNode *&T,int m){
int len=prevec.size();
if(len>1){
int root=prevec[0];
vector<int> Linvec;
vector<int> Rinvec;
int mid=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
if(invec[i]!=root){
Linvec.push_back(invec[i]);
mid++;
}else
break;
}
for(int i=mid+1;i<len;i++)
Rinvec.push_back(invec[i]);
vector<int> Lprevec;
vector<int> Rprevec;
for(int i=1;i<mid+1;i++)
Lprevec.push_back(prevec[i]);
for(int i=mid+1;i<len;i++)
Rprevec.push_back(prevec[i]);
if(m==-1){
T=new TreeNode(root);
PreIndfs(Lprevec,Linvec,T,1);
PreIndfs(Rprevec,Rinvec,T,0);
}else{
TreeNode *temp=new TreeNode(root);
if(m==1)
T->left=temp;
else if(m==0)
T->right=temp;
PreIndfs(Lprevec,Linvec,temp,1);
PreIndfs(Rprevec,Rinvec,temp,0);
}
}else if(len==1){
TreeNode *temp=new TreeNode(prevec[0]);
if(m==1)
T->left=temp;
else if(m==0)
T->right=temp;
}
}
int getHigh(TreeNode *T){ //获取二叉树的高度
if(T!=NULL){
int l=1+getHigh(T->left);
int r=1+getHigh(T->right);
if(l>r)
return l;
else
return r;
}else
return 0;
}
void mirroTree(TreeNode *T){ //二叉树镜像
if(T!=NULL){
TreeNode *temp=T->left;
T->left=T->right;
T->right=temp;
mirroTree(T->left);
mirroTree(T->right);
}
}
int main(){
TreeNode t1(1),t2(2),t3(3),t4(4),t5(5),t6(6),t7(7);
t1.left=&t2;
t1.right=&t3;
t2.left=&t4;
t2.right=&t5;
t3.left=&t6;
t3.right=&t7;
TreeNode *root=&t1;
preVist(root);
cout<<endl;
preVistf(root);
cout<<endl;
inVist(root);
cout<<endl;
inVistf(root);
cout<<endl;
int preA[7]={1,2,4,5,3,6,7};
int inA[7]={4,2,5,1,6,3,7};
vector<int> prevec(preA,preA+7);
vector<int> invec(inA,inA+7);
TreeNode *T1;
PreIndfs(prevec,invec,T1,-1);
preVist(T1);
cout<<endl;
inVist(T1);
cout<<endl;
cout<<getHigh(T1)<<endl;
mirroTree(T1);
preVist(T1);
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
}
二叉树最长路径和最大权值路径
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int n):val(n){
left=NULL;
right=NULL;
}
};
void preVist(TreeNode *T){ //递归先序遍历
if(T!=NULL){
cout<<T->val<<" ";
preVist(T->left);
preVist(T->right);
}
}
int getHeight(TreeNode *T){ //获取从树的某一结点到叶子结点的最长路径
if(T==NULL)
return 0;
else{
int l=getHeight(T->left);
int r=getHeight(T->right);
return 1+(l>r?l:r);
}
}
void maxPath(TreeNode *T,int &maxpath){ //计算二叉树的最长路径
if(T!=NULL){
int l=getHeight(T->left);
int r=getHeight(T->right);
if(maxpath<l+r) maxpath=l+r;
maxPath(T->left,maxpath);
maxPath(T->right,maxpath);
}
}
int getWeight(TreeNode *T){ //获取树的某一结点到叶子结点的权值最大路径
if(T==NULL)
return 0;
else{
int l=getWeight(T->left);
int r=getWeight(T->right);
return T->val+(l>r?l:r);
}
}
void maxWeight(TreeNode *T,int &maxweight){ //计算二叉树的最大权值路径
if(T!=NULL){
int l=getWeight(T->left);
int r=getWeight(T->right);
if(maxweight<T->val+l+r) maxweight=T->val+l+r;
maxWeight(T->left,maxweight);
maxWeight(T->right,maxweight);
}
}
int main(){
TreeNode t1(1),t2(2),t3(3),t4(4),t5(5),t6(6),t7(7),t8(8);
t1.left=&t2;
t1.right=&t3;
t2.left=&t4;
t2.right=&t5;
t3.left=&t6;
t3.right=&t7;
t6.right=&t8;
TreeNode *root=&t1;
preVist(root);
cout<<endl;
int maxpath=0;
maxPath(root,maxpath);
cout<<maxpath<<endl;
int maxweight=0;
maxWeight(root,maxweight);
cout<<maxweight<<endl;
system("pause");
}